Windenergie 2 - Wake 1
05 November 2025, Po Wen Cheng
Questions at the beginning
- Which distribution is the most suitable one for extreme wind?
- Gumbel Distribution
- Which of the fitting methods is less sensitive to outliers
- What is the return period in years if we use a Gumbel distribution for the yeatly maxima and the exceedence probability is 0.1
- 10 Years
- What is the probability of occurence of the 10 year extreme wind speed happening two years in a row, in percent?
- 1 %
- Which are the two distribution parameters of the Gumbel distribution?
- Scale Parameters
- Shape Parameters
- The second statistical moment of a distribution function is related to the...?
- Variance
- What is the wake of wind turbines and what is the effect of wake on the power production?
Basics
Wind leaving the turbine has less energy, less wind speed and less turbulence, it is called the wake
In wind energy wake, flow on the wind-turbine and wind-farm scale is most relevant. Airfoil scale, mesoscale and macroscale are less relevant
The higher the thrust on the rotor, the lower the wind velocity in the wake and the larger the shear
Actuator disk: One-dimensional theory
The wind speed in the wake depends consequently on the thrust coefficient of each wind turbine
corrolation between the wind speeds can be written as:
$$ \frac{v_3}{v_1} = \sqrt{(1-c_t)} $$
Characteristics
Wake in the full load region of the wind turbine does not matter, as there is too much energy anyway. It only matters in the partial load region
Velocity Deficit and Wake Rotation
Velocity deficit due to the operation of the wind turbine and wind - structure interactions\
Downstream of the turbine low velocity fuid inside and the high velocity fluid outside the wake are mixed due to presence of the atmospheric turbulence
Far wake is most important to predict power loss
- The wake expands die to the mass conservation
- Velocity deficit is reduced due to the mixing of undisturbed flow with the wake
The maximum velocity deficit is reached after 1-2 D distance from the rotor, but for low ambient turbulence the maximum velocity deficit may be located further downstream.
$\rightarrow$ Reason: The turbulent mixing is lower and the flow velocity takes longer to recover.
(D = Rotor Diameter)
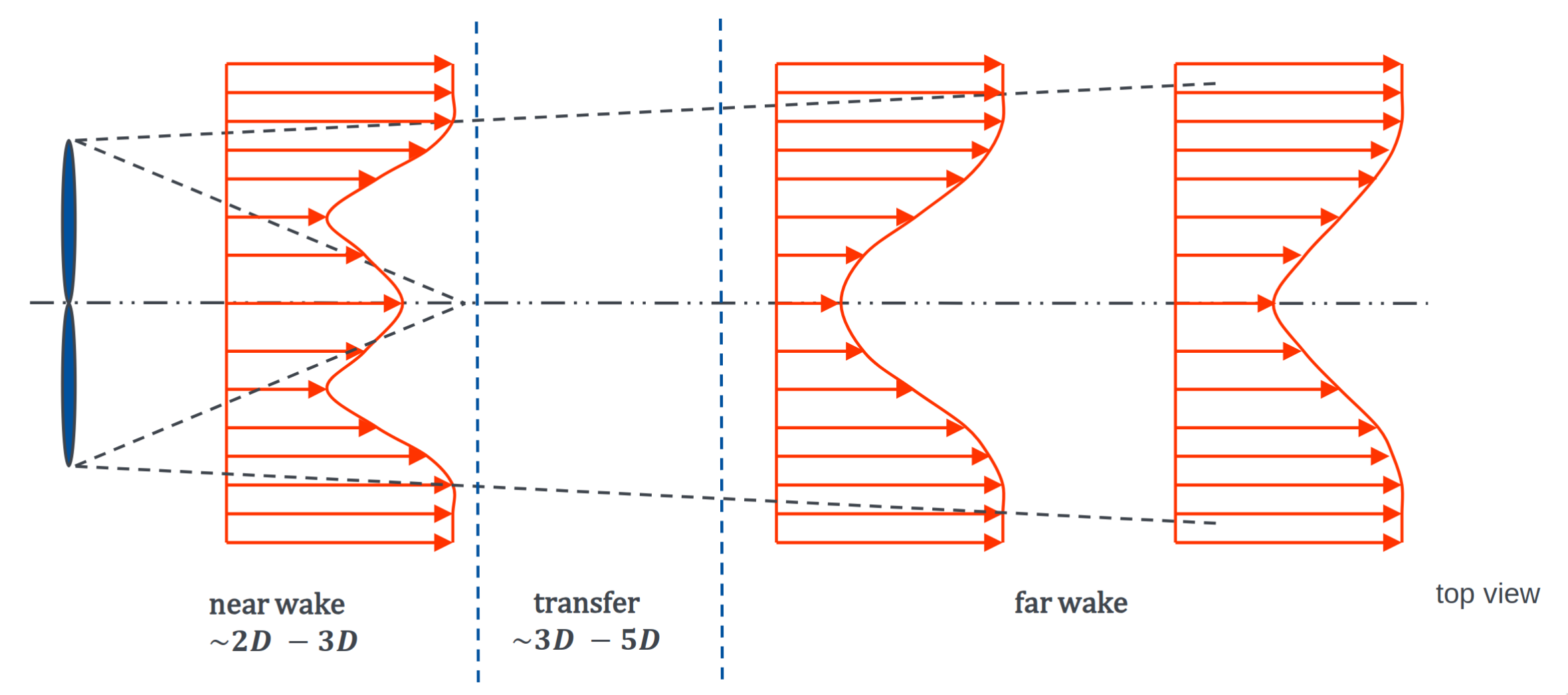
Near Wake
The shape of the flow field in the near wake is affected by the turbine geometry, such as blade geometry, nacelle and hub geometry
To understand near wake, it is neccessary to obtain the turbine specific information
Near wake length is influenced by
- turbulence intensity of the incoming flow
- mechanical shear generated by the turbine
- turbine tip-speed ratio
Far wake
The velocity difference between the air inside and outside the wake leads to a shear layer. Because of the ambient shear flow, the turbulence in the shear layer is non-uniform, consequently the turbulence intensity in the upper part is larger than in the lower part. In the near wake two peaks in the turbulence intensity appear, in the far wake they are not discernible
Most important factors fot size of the turbine wake:
- Thrust
- Convective Boundary Layer / Stable Boundary Layer (Turbulence intensity)