Windenergie 2 - Site Assessment
15 October 2025, Po Wen Cheng
Exam
- Date not known yet
- No tools in Questionaire, Two sheets of A4 handwritten or printed, Calculator in rest of exam
- Exam very simmilar to Excercises - so do them
- Verständnisfragen 30 min
- Rechenteil 60 min
Misc
- Windenergielabor tomorrow 2pm in Allmandring 5b in 0.42
- Wind Energy Project student group meeting wednesday, 9:45 in Allmandring 5b in 0.42, more information on Ilias
Literature


Site characterization
Identify potentially windy areas which also possess all the necessary requirements for the errection of wind turbines
- Identification of potential wind development areas
- Inspection and ranking of the candidate site and
- Selection of actual tower location(s) within the candidate site
Standard measurements for site assessment are wind speed, wind direction, atmospheric pressure, air temperature, relative air humidity.
wind atlas website is not sufficient, because it is too uncertain
Data has to be collected over at least a year, usually by Met Mast with sensors on several heights
The highest measured height should be at least 2/3 of the intended hub height. Sensors include:
- Cup anemometer
- Wind vane
- Sonic anemometer
- Temperature sensor
- Pressure Sensor
Sometimes, remote measurements are used (Lidar and Sodar)
Wind flow models
Two approaches to model the velocity profile of the atmospheric boundary layer
- Using logarithmic approximation
- Using the power law approximation
Atmospheric stability
- Usually unstable during summer: air close to the ground is warmer and wants to rise up, forming large convection cells, little wind shear
- Usually stable during winter: cold, heavy air on the ground, turbulence dominated by the friction with the ground, large wind shear
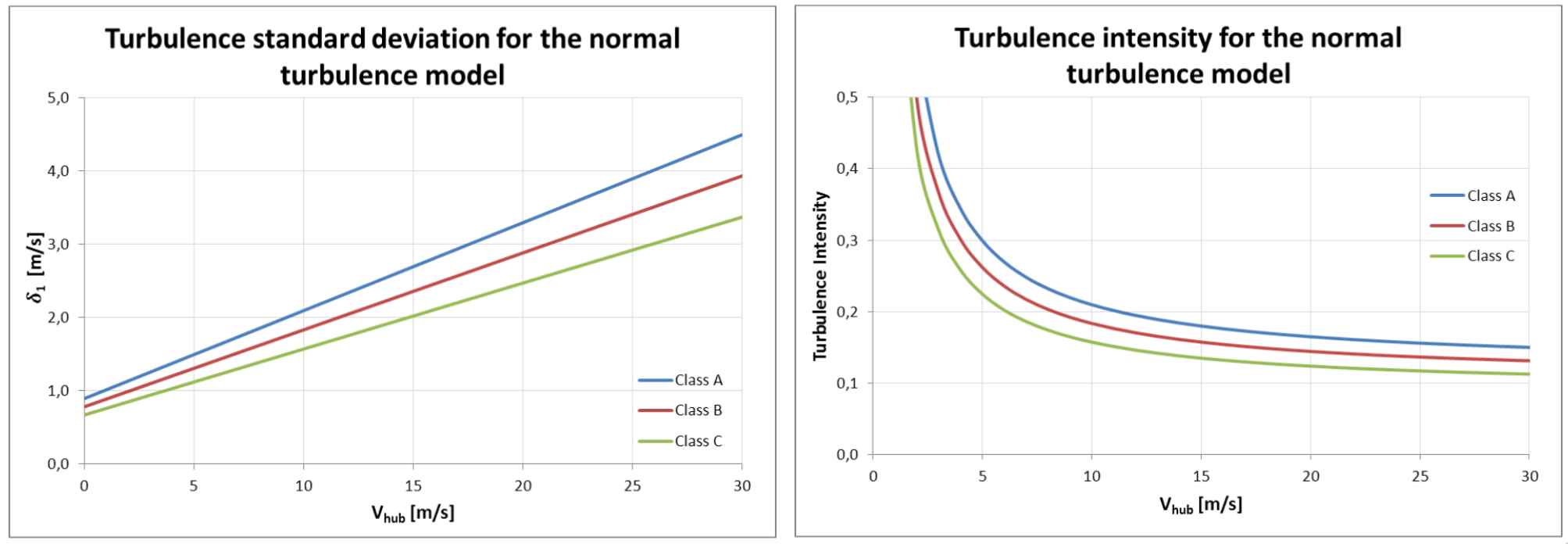
Low turbulence intensity if function of surface roughness, atmospheric stability, distance above ground, wakes from the turbines
High tubulences can reduce the turbines expected lifetime, e.g. because turbine has to keep power constant by pitching constantly
IEC turbulence classes to classify wind turbines into wind speed and turbulence categories I, II, III
Modeling used to extrapolate measurements to other locations, possible methods are:
- Conceptual models
- Based on practical experience and boundary layer meterology
- Experimental models
- Older
- Terrain model in wind tunnel for testing
- Statistical models
- More modern
- Based entirely on measurements
- Numerical Wind Flow Models
- Uses physics, not statistics
- Mass consistent models
- computational fluid dynamics
- Jackson-Hunt models
- Standard today: WAsP model by Risø, Denmark, still not good enough with very complex terrain, then you need CFD
Measure correlate predict (MCP)
No time, will be done next lecture